Spring Security
Spring Security入门
一、Spring Security简介
1. 概述
Spring Security 是 Spring 家族中的一个安全管理框架,应用程序的两个主要区域是“认证”和“授权”(或者访问控制)
- 认证:
系统提供的用于识别用户身份的功能,通常提供用户名和密码进行登录其实就是在进行认证,认证的目的是让系统知道你是谁。
- 授权:
用户认证成功后,需要为用户授权,其实就是指定当前用户可以操作哪些功能。
- 权限数据模型
前面已经分析了认证和授权的概念,要实现最终的权限控制,需要有一套表结构支撑:
用户表t_user、权限表t_permission、角色表t_role、菜单表t_menu、用户角色关系表t_user_role、角色权限关系表t_role_permission、角色菜单关系表t_role_menu。
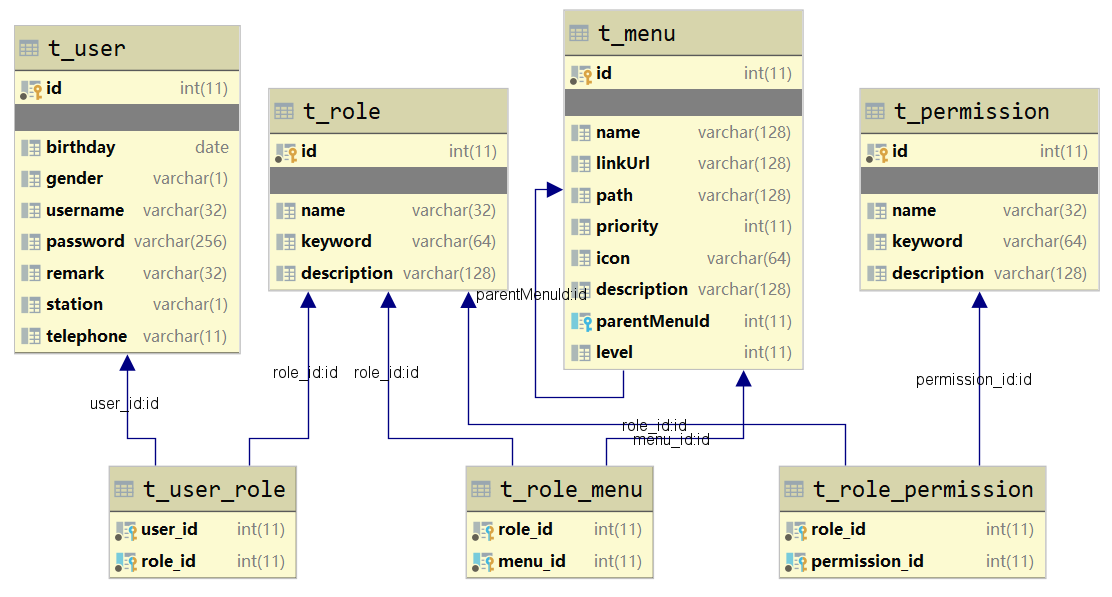
上述的7张表就构成了RBAC权限模型:

2. 快速入门
1. 创建maven工程,pom文件导入依赖,创建启动类
<!--继承boot父工程-->
<parent>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<version>2.6.0</version>
</parent>
<dependencies>
<!--web起步依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--SpringSecurity起步依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-security</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>启动类:
@SpringBootApplication
public class SsApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SsApplication.class, args);
}
}2. 编写controller
@RestController
public class HelloController {
@GetMapping("/hello")
public String hello(){
System.out.println("hello...");
return "Hello SpringSecurity~";
}
}3. 访问controller
- 会出现登录页面,表明springsecurity已经开始工作
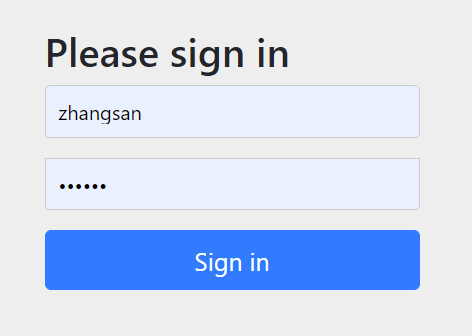
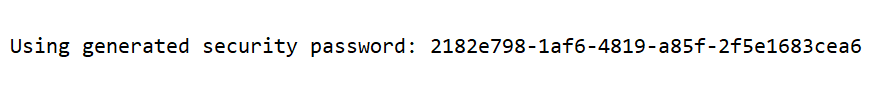
- 输入默认的用户名: user , 密码通过控制台可以找到springsecurity产生的密码
3. 细节处理
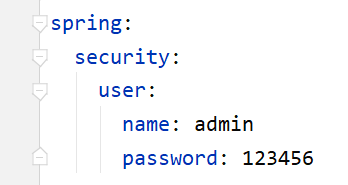
3.1 自定义用户名和密码
在application.yml里面可以配置自定义的用户名和密码
3.2 修改日志级别
默认打印的springsecurity的日志级别是 info级别,如果想观察到更详细的日志信息,可以在application.yml 里面修改日志的打印级别 。 如果info看不到日志,可以尝试再设置低一些级别:
比如: debug 或者 trace 级别
log.info()、log.error()
日志级别:fatal>error>warn>info>debug>trace
logging:
level:
org:
springframework:
security: debug4. 原理
4.1 SpringBoot自动配置
默认情况下,只要在SpringBoot项目里面添加了SpringSecurity依赖,那么 SpringSecurity 即会自动工作。这个自动生效的配置是由SpringBoot来完成的。
- 在启动类身上的注解
@SpringBootApplication即是一切自动配置的开始 - 进入该注解内部有一个注解 :
@EnableAutoConfiguration, 表示启动自动配置 - 在
@EnableAutoConfiguration注解里面,导入了AutoConfigurationImportSelector自动配置导入选择器 - 在这个自动导入选择器类
AutoConfigurationImportSelector中的getCandidateConfigurations可以看到自动导入的类位于META-INF/spring.factories文件中。 - 该文件位于 SpringBoot 的autoconfigure包中
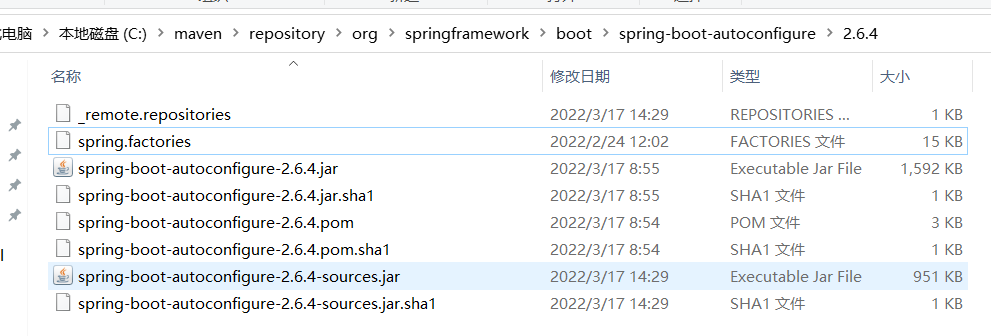
- 在spring.factories文件中搜索security关键字,找到执行 SpringSecurity 自动配置的类:SecurityAutoConfiguration
- 在SecurityAutoConfiguration里面发现它在上面使用 @Import导入 SpringBootWebSecurityConfiguration 类。
- SpringBootWebSecurityConfiguration 会对所有的请求进行拦截,自此springsecurity的自动配置解析完毕:
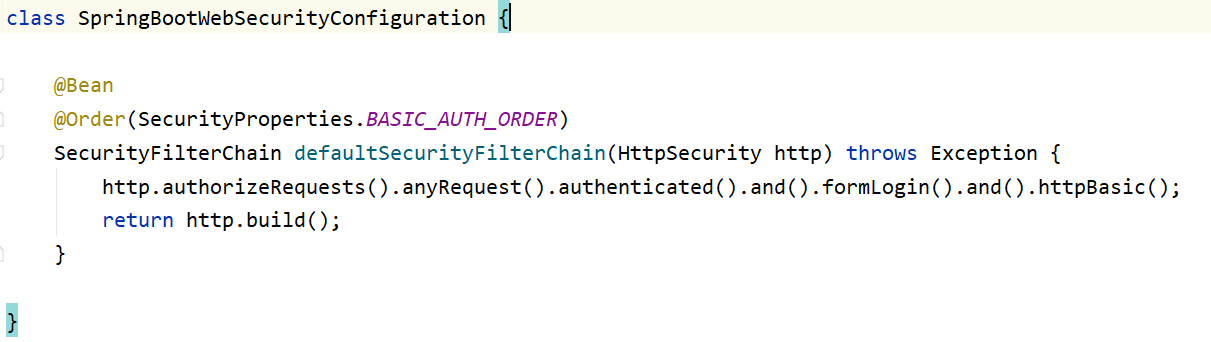
4.2 SpringSecurity原理分析
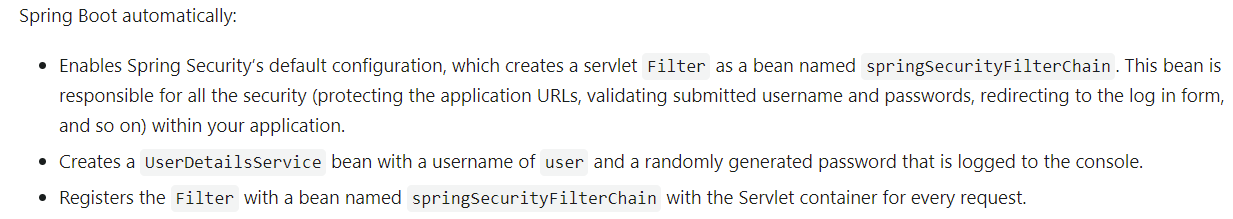
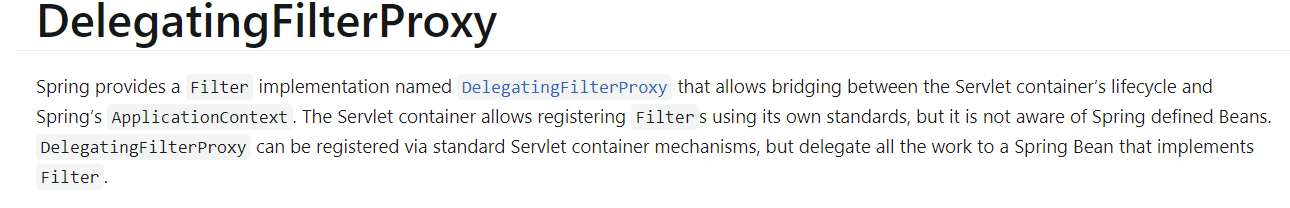
SpringSecurity的核心即是: 过滤器Filter , 翻开SpringSecurity的官方文档,找到如下说明:
- 这个SecurityFilterChain对象使用位置:WebSecurityConfiguration中的springSecurityFilterChain方法中
- 通过debug发现,总共有15个过滤器需要配置,这些过滤器各司其职,每个过滤器负责的功能都不一样!
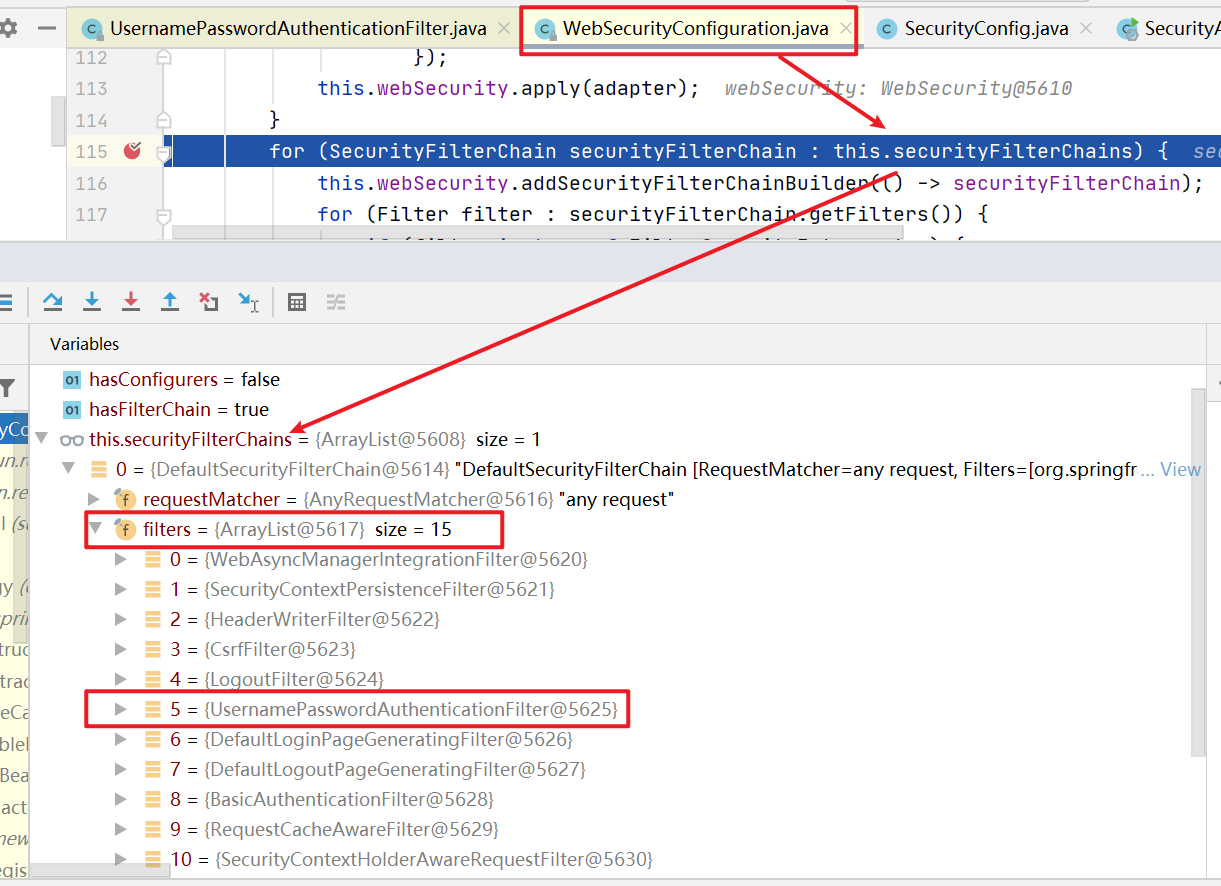
重点关注的过滤器:UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter
- 参照官方文档的说明,可以看到有对 SpringSecurity 过滤器的描述、以及流程解释:
二 、认证授权
在DefaultWebSecurityCondition 里面存在注解 @ConditionalOnMissingBean({WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter.class,… }) 表明如果在JVM中缺失 WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter 则会启用默认的springsecurity的认证和授权流程。 所以如果我们希望自己执行认证和授权,那么编写一个类,继承 WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter 即可。
1. 内存方式
一般在开发当中,我们都会选择自己来认证授权!
1.1. 定义配置类
//为了让spring发现我们写的配置类,需要加上 @Configuration
@Configuration
public class SecurityConfigure extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
}1.2. 重写方法
1.2.1 认证方法
/**
* 认证
* 什么样的账号和密码, 是什么样的角色
* @param auth
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
//内存中的认证:{noop}代表密码不加密,直接使用明文存储
auth.inMemoryAuthentication()
.withUser("zhangsan")
.password("{noop}123")
.roles("ZS")
.and()
.withUser("admin")
.password("{noop}666")
.roles("ADMIN");
}1.2.2 授权方法
/**
* 授权:
* 1. 什么样的请求地址允许直接访问
* 2. 什么样的请求需要有相应角色权限才能访问
* 3. 其他的请求全部要求认证通过之后才能访问。
* @param http
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.authorizeRequests()
//直接访问,不需要登录的请求
.antMatchers("/login.html").permitAll()
//需要登录角色ADMIN,才能访问的请求
.antMatchers("/show01").hasRole("ADMIN")
//需要登录角色ZS或LS,才能访问的请求
.antMatchers("/show02").hasAnyRole("ZS", "LS")
//其他请求,只需要登录就可以访问
.anyRequest().authenticated()
//and 用来拼接配置
.and()
//表示使用默认SpringSecurity的登录页面
.formLogin();
}1.2.3 异常处理
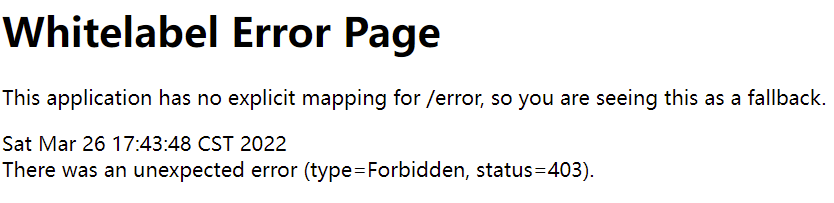
当我们已经登录,但是访问并不具有访问权限的资源时,那么会出现403 的异常:
- 解决办法: 在授权方法里面添加关于异常的处理办法:
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.authorizeRequests()
//直接访问,不需要登录的请求
.antMatchers("/login.html").permitAll()
//需要登录角色ADMIN,才能访问的请求
.antMatchers("/show01").hasRole("ADMIN")
//需要登录角色ZS或LS,才能访问的请求
.antMatchers("/show02").hasAnyRole("ZS", "LS")
//其他请求,只需要登录就可以访问
.anyRequest().authenticated()
//and 用来拼接配置
.and()
//表示使用默认SpringSecurity的登录页面
.formLogin();
//异常处理:方式一
/*AccessDeniedHandlerImpl accessDeniedHandler = new AccessDeniedHandlerImpl();
accessDeniedHandler.setErrorPage("/error.html");
http.exceptionHandling().accessDeniedHandler(accessDeniedHandler);*/
//异常处理:方式二
/*http.exceptionHandling().accessDeniedHandler(new MyAccessDeniedHandler());*/
//异常处理:方式三
/*http.exceptionHandling().accessDeniedHandler(new AccessDeniedHandler() {
@Override
public void handle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, AccessDeniedException accessDeniedException) throws IOException, ServletException {
response.setContentType("text/json;charset=utf-8");
response.getWriter().write(JSON.toJSONString(R.error("权限不足!-3")));
}
});*/
//异常处理:方式四
http.exceptionHandling().accessDeniedHandler((request, response, exception)->{
response.setContentType("text/json;charset=utf-8");
response.getWriter().write(JSON.toJSONString(R.error("权限不足!-4")));
});
}
- 异常处理类
public class MyAccessDeniedHandler implements AccessDeniedHandler {
@Override
public void handle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, AccessDeniedException accessDeniedException)
throws IOException, ServletException {
//response.setContentType("text/html;charset=utf-8");
response.setContentType("application/json;charset=utf-8");
response.getWriter().write("权限不足-1,禁止访问!");
}
}
1.3 自定义登录页面
默认springsecurity的登录操作,会被过滤器: UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter 拦截,它内部有几个判定: ==请求方式是 post==, 请求地址是 /login , 用户名参数是: username , 密码参数名是: password
请求方式不能修改之外,其他的都可以修改
1.3.1 定义登录页面
<form action="/login" method="post">
用户名: <input type="text" name="username"/><br/>
密 码: <input type="password" name="password"/><br/>
<input type="submit" value="登录"/>
</form>1.3.2 配置
/**
* 授权:
* 1. 什么样的请求地址允许直接访问
* 2. 什么样的请求需要有相应角色权限才能访问
* 3. 其他的请求全部要求认证通过之后才能访问
* @param http
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
//...
http.formLogin()
//登录页面
.loginPage("/login.html")
//用户名参数名称
.usernameParameter("username")
//密码参数名称
.passwordParameter("password")
//登录的请求地址
.loginProcessingUrl("/login")
//登录成功之后默认跳转的页面,设置true的话,则强制跳转到该页面
.defaultSuccessUrl("/index.html",true)
//登录失败之后跳转的页面
.failureForwardUrl("/login.html")
//禁用 csrf 跨站伪造请求
.and().csrf().disable();
//【扩展】前后端分离返回形式
/*http.formLogin()
//登录页面
.loginPage("/login.html")
//用户名参数名称
.usernameParameter("username")
//密码参数名称
.passwordParameter("password")
//登录的请求地址
.loginProcessingUrl("/login")
//登录成功处理器
.successHandler((request, response, authentication)->{
response.setContentType("text/json;charset=utf-8");
response.getWriter().write(JSON.toJSONString(R.success("login success!")));
})
//登录失败处理器
.failureHandler((request, response, exception)->{
response.setContentType("text/json;charset=utf-8");
response.getWriter().write(JSON.toJSONString(R.success("login fail!")));
})
//禁用 csrf 跨站伪造请求
.and().csrf().disable();*/
//...
}1.3.3 csrf
CSRF(Cross-site request forgery),中文名称:跨站请求伪造,缩写为:CSRF/XSRF。
一般来说,攻击者通过伪造用户的浏览器的请求,向访问一个用户自己曾经认证访问过的网站发送出去,使目标网站接收并误以为是用户的真实操作而去执行命令。常用于盗取账号、转账、发送虚假消息等。
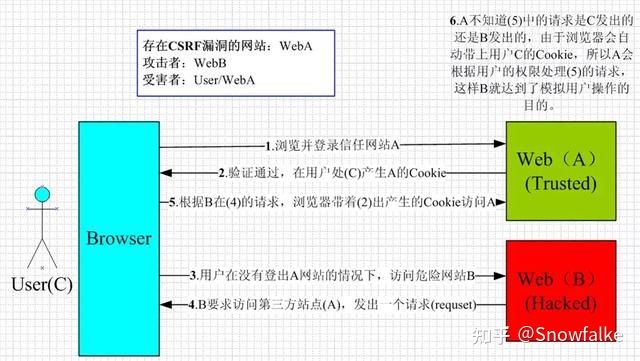
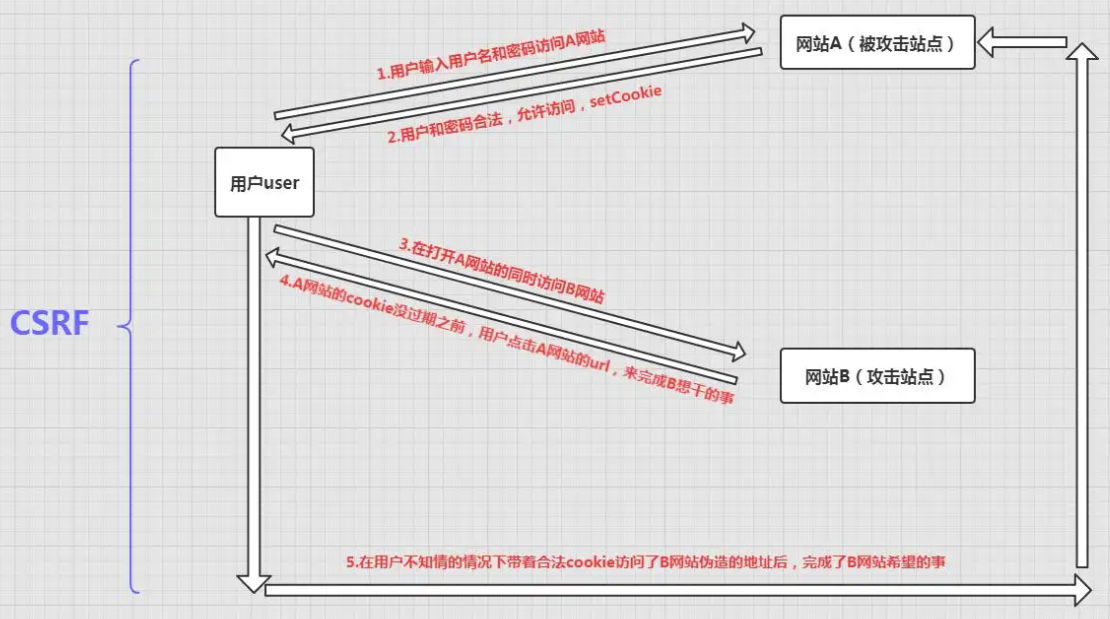
参考网址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_45803593/article/details/124727762
1.3.4 退出登录
/**
* 授权:
* 1. 什么样的请求地址允许直接访问
* 2. 什么样的请求需要有相应角色权限才能访问
* 3. 其他的请求全部要求认证通过之后才能访问
* @param http
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
//...
http.formLogin()
//登录页面
.loginPage("/login.html")
//用户名参数名称
.usernameParameter("username")
//密码参数名称
.passwordParameter("password")
//登录的请求地址
.loginProcessingUrl("/login")
//登录成功之后默认跳转的页面,设置true的话,则强制跳转到该页面
.defaultSuccessUrl("/index.html",true)
//登录失败之后跳转的页面
.failureForwardUrl("/login.html")
//禁用 csrf 跨站请求伪造
.and().csrf().disable()
//退出登录配置
.logout()
//退出的请求地址
.logoutUrl("/logout")
//退出之后跳转的页面
.logoutSuccessUrl("/login.html");
//...
}1.4. 密码加密
1.4.1 加密方式
在springsecurity里面,支持的加密方式有很多, 具体可以在 PasswordEncoderFactories 里面查看。官方推荐使用 bcrypt 加密方式。

MD5:摘要算法采用Hash处理,加密方式不可逆(明文–>密文), 但是每次加密的结果都是一样的
针对它的缺陷,解决方式:
方式一:加密多次 至少3次以上
方式二:Md5(password+salt) salt:随机字符串 UUID
bcrypt:将salt随机并混入最终加密后的密码,验证时也无需单独提供之前的salt,从而无需单独处理salt问题
SpringSecurity 中的BCryptPasswordEncoder方法采用 SHA-256 +随机盐+密钥 对密码进行加密。SHA系列是Hash算法,不是加密算法,使用加密算法意味着可以解密(这个与编码/解码一样),但是采用Hash处理,其过程是不可逆的。
(1)加密(encode):注册用户时,使用SHA-256+随机盐+密钥把用户输入的密码进行hash处理,得到密码的hash值,然后将其存入数据库中。
(2)密码匹配(matches):用户登录时,密码匹配阶段并没有进行密码解密(因为密码经过Hash处理,是不可逆的),而是使用相同的算法把用户输入的密码进行hash处理,得到密码的hash值,然后将其与从数据库中查询到的密码hash值进行比较。如果两者相同,说明用户输入的密码正确。
为什么处理密码时要用hash算法,而不用加密算法?因为这样处理即使数据库泄漏,黑客也很难破解密码。
- 加密结果解释
$2a$10$7Pb7IxzTL1bXA9a/A92y.OPBqYjqFZpnw6poI8NGYAkHj4IBe0Zhu加密后字符串的长度为固定的60位。其中:
$是分割符,无意义;
2a是bcrypt加密版本号:2a
10是循环10次加盐加密:10
$符号后接下来的22位是salt值:7Pb7IxzTL1bXA9a/A92y.O
剩下的字符串就是密码的密文了:PBqYjqFZpnw6poI8NGYAkHj4IBe0Zhu
1.4.2 具体应用
要想使用BCrypt密码加密其实很简单,只需要在配置类中定义一个方法,返回 BcryptPasswordEncoder 对象即可,并且不要忘记了对认证的用户密码进行加密处理。
用户在输入密码登录时,SpringSecurity就会自动对用户输入的密码使用BCrypt进行加密,然后和内存|数据库中存储的用户密码进行比对 注意:内存|数据库中存储的用户密码也要使用BCrypt进行加密
密码加密使用步骤:
1.对用户输入的密码进行加密
2.对内存|数据库中存储的密码进行加密
注意:两边的加密方式要一致
- 添加方法
/**
* 1.定义一个方法:创建 BCryptPasswordEncoder 对象,并且交由spring容器管理
* 2.用户在输入密码登录时,SpringSecurity就会自动对用户输入的密码使用 BCrypt 进行加密
* 3.然后在进行登录认证时就会和内存|数据库中存储的用户密码进行比对
* **注意:**内存|数据库中存储的用户密码也要使用 BCrypt 进行加密之后再存储
* @return
*/
@Bean //bean注解 代表该方法会创建出一个bean对象,并且将该对象交由spring容器管理
public BCryptPasswordEncoder bp() {
return new BCryptPasswordEncoder();
}- 认证处理
/**
* 认证
* 什么样的账号和密码, 是什么样的角色
* @param auth
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
//基于内存的认证
auth.inMemoryAuthentication()
.withUser("admin")
// .password("{noop}666")
.password(bp().encode("666"))
.roles("ADMIN")
.and()
.withUser("zhangsan")
// .password("{noop}123")
.password(bp().encode("123"))
.roles("ZS")
.and()
.withUser("lisi")
// .password("{noop}456")
.password(bp().encode("456"))
.roles("LS");
}2. 数据库方式
2.1 准备数据库
# 创建数据库day36_ss 并使用该数据库
CREATE DATABASE day36_ss;
USE day36_ss;
# 创建用户表
create table t_user(
id bigint primary key auto_increment ,
username varchar(25) ,
password varchar(65) ,
name varchar(25)
)ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4;
# 创建角色表
create table t_role(
id int primary key auto_increment,
name varchar(25) ,
keyword varchar(25)
)ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4;
# 创建用户角色表
create table t_user_role(uid bigint , rid int )ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4;
# 添加外键
alter table t_user_role add constraint FK_user_ur foreign key (uid) references t_user(id);
alter table t_user_role add constraint FK_role_ur foreign key (rid) references t_role(id);
# 添加数据 密码是 123456 加密后的效果
insert into t_user values ( null , 'zhangsan' , '$2a$10$ezVuPO6NaUsQZ66p7y0QSeWfO6s.Qoz01vbTcI2vlcuLXy8Wk.DOy' , '张三');
insert into t_user values ( null , 'lisi' , '$2a$10$ezVuPO6NaUsQZ66p7y0QSeWfO6s.Qoz01vbTcI2vlcuLXy8Wk.DOy' , '李四');
insert into t_role values ( null , '管理员' , 'ROLE_ADMIN' );
insert into t_role values ( null , '普通员工' , 'ROLE_USER' );
insert into t_user_role value( 1 , 1 );
insert into t_user_role value( 2 , 2 );2.2:创建项目,添加mybatisplus、mysql驱动、lombok依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>com.baomidou</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-plus-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>3.4.2</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
</dependency>2.3:application.yml中配置数据源
spring:
datasource:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/day44?useSSL=false&serverTimezone=UTC
username: root
password: 12342.4 准备实体类
- User
@Data
public class User {
private Long id ;
private String username;
private String password;
private String name;
//用于记录用户的角色信息,一个用户可以有多个角色身份。
private List<Role> roleList;
}
- Role
@Data
public class Role {
private Long id ;
private String name;
private String keyword;
}
2.5 准备dao
- UserDao
@Mapper
public interface UserDao extends BaseMapper<User> {
/**
* 根据用户名查询用户
* @param username
* @return
*/
User findByUsername(String username);
}
- UserDao.xml
位于: resources/mapper/
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.itheima.dao.UserDao">
<resultMap id="userMap" type="com.itheima.bean.User">
<result property="username" column="username" />
<result property="password" column="password" />
<!--
collection:配置一对多 将查询出来的每条角色信息封装到一个Role对象中 最终存入到roleList集合中
collection属性的封装规则:
property="roleList": 指定这是哪个集合属性
ofType: 指定集合内封装的JavaBean类型(集合内装的什么),这里即为 Role 类
-->
<collection property="roleList" ofType="com.itheima.bean.Role">
<result property="name" column="name"/>
<result property="keyword" column="keyword"/>
</collection>
</resultMap>
<select id="findByUsername" resultMap="userMap">
SELECT
u.username,
u.password,
r.name,
r.keyword
FROM
t_user u
LEFT JOIN t_user_role ur
ON u.id = ur.uid
LEFT JOIN t_role r
ON r.id = ur.rid
where username=#{username}
</select>
</mapper>- application.yml (如果xml文件所在包名与dao所在包名不一致那么需要配置映射)
mybatis-plus:
type-aliases-package: com.itheima.bean
mapper-locations: classpath:mapper/*.xml2.6 准备配置类
@Service
public class UserDetailServiceImpl implements UserDetailsService {
@Autowired
private UserDao userDao;
@Override
public UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String username) throws UsernameNotFoundException {
//1. 根据用户名查询用户
User user = userDao.findByUsernameUser(username);
System.out.println("user = " + user);
//2. 构建返回
List<GrantedAuthority> list = new ArrayList<>();
List<Role> roleList = user.getRoleList();
for (Role role : roleList) {
list.add(new SimpleGrantedAuthority(role.getKeyword()));
}
//返回用户详情信息
return new org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.User(
user.getUsername() ,
user.getPassword() ,
list);
}
}
2.7 修改认证方法
@Configuration
public class SecurityConfigure extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Autowired
private UserDetailServiceImpl us;
@Bean
public BCryptPasswordEncoder bp (){
return new BCryptPasswordEncoder();
}
/*
认证:
什么样的账号和密码, 是什么样的角色
*/
@Override
protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
auth.userDetailsService(us);
}
//...授权方法
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/**/*.html","/**/*.css","/**/*.js").permitAll()
.antMatchers("/show").hasRole("ADMIN")
.antMatchers("/show02").hasRole("USER")
.anyRequest().authenticated()
.and().formLogin()
.loginPage("/login.html")
.loginProcessingUrl("/login").defaultSuccessUrl("/index.html",true).failureForwardUrl("/login.html")
.and().csrf().disable()
.logout().logoutUrl("/logout").logoutSuccessUrl("/login.html")
//403异常处理
.and().exceptionHandling().accessDeniedHandler(new AccessDeniedHandler() {
@Override
public void handle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, AccessDeniedException accessDeniedException) throws IOException, ServletException {
response.setContentType("text/html;charset=UTF-8");
response.getWriter().print("权限不足 禁止访问");
}
});
}
}3. 注解动态授权
springsecurity允许程序员在Controller方法上使用注解来动态授权,即配置角色|权限到方法上。表明需要具备什么样的角色身份或者是权限,才允许访问该方法!
- 1.在方法上使用 @PreAuthorize 进行调用 权限拦截
//表明调用方法需具有该角色身份。
@PreAuthorize("hasRole('ADMIN')")
@RequestMapping("/show66")
public String show66(){
System.out.println("执行了show66方法!~~!");
return "show ... success...";
}- 2.要想让注解生效,需要在启动类上面设置注解
//启用全局方法注解
@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(prePostEnabled = true)
@SpringBootApplication
public class Demo1HelloworldApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Demo1HelloworldApplication.class, args);
}
}三 、整合项目
1. 添加依赖
<!--添加springsecurity-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-security</artifactId>
</dependency>2. 创建表
可以直接执行资料中提供的sql脚本:role.sql、employ_role.sql
- 角色表
create table role
(
id bigint auto_increment primary key,
name varchar(100) null,
keyword varchar(25) null
)ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4;- 员工角色表
create table if not exists employee_role
(
eid bigint null,
rid bigint null,
constraint user_role_role_id_fk
foreign key (rid) references role (id),
constraint user_role_user_id_fk
foreign key (eid) references employee (id)
)ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4;
3. 编写实体类
- Role
package com.itheima.bean;
import lombok.Data;
@Data
public class Role {
private Long id ;
private String name;
private String keyword;
}- EmployeeRole
/**
* 员工角色关系表实体类
*/
@Data
public class EmployeeRole {
private Long eid;
private Long rid;
}- Employee
让Employee实现UserDetails 这样在认证方法返回即可只返回Employee对象即可
因为它里面包含了权限内容
@Data
public class Employee implements Serializable , UserDetails {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
@TableField(exist = false)
private List<Role> roleList = new ArrayList<>();
//原有属性省略...
//封装角色集合信息到List<GrantedAuthority>中
@Override
public Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> getAuthorities() {
List<GrantedAuthority> list = new ArrayList<>();
roleList.forEach(r->{
list.add(new SimpleGrantedAuthority(r.getKeyword()));
});
return list;
}
//没有过期
@Override
public boolean isAccountNonExpired() {
return true;
}
//没有被锁定
@Override
public boolean isAccountNonLocked() {
return true;
}
//认证后永不过期
@Override
public boolean isCredentialsNonExpired() {
return true;
}
//是否可用 status=1为正常状态,status=0禁用状态
@Override
public boolean isEnabled() {
return this.status == 1;
}
}4. 编写Dao
public interface EmployeeDao extends BaseMapper<Employee> {
/**
* 根据用户名来查询员工信息及角色身份列表信息
* @param username
* @return
*/
Employee findByUsername(String username);
}5. 编写映射文件
- EmployeeDao.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.itheima.dao.EmployeeDao">
<resultMap id="empMap" type="Employee">
<id property="id" column="id"/>
<result property="name" column="name"/>
<result property="username" column="username"/>
<result property="password" column="password"/>
<result property="status" column="status"/>
<!--
collection 配置一对多中的对象集合属性,数据填充
property: 指定集合属性名称
ofType: 指定集合内封装的JavaBean类型(集合内装的什么对象)
-->
<collection property="roleList" ofType="Role">
<result property="name" column="r_name"/>
<result property="keyword" column="keyword"/>
</collection>
</resultMap>
<select id="findByUsername" resultMap="empMap">
SELECT
e.*,
r.name r_name,
r.keyword
FROM
employee AS e
INNER JOIN employee_role er
ON e.id = er.eid
INNER JOIN role r
ON er.rid = r.id
WHERE e.username = #{username}
</select>
</mapper>- application.yml
#别名映射、实体类包名映射
mybatis-plus:
mapper-locations: classpath:/mapper/*.xml
type-aliases-package: com.itheima.bean6. 编写过滤器类
/**
* 自己定义的过滤器,用来顶替springsecurity的账号密码校验的过滤器
*/
public class SecurityLoginFilter extends UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter {
@Override
public Authentication attemptAuthentication(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws AuthenticationException {
//如果登录请求方式不是post请求 就抛出异常
if (!request.getMethod().equals("POST")) {
throw new AuthenticationServiceException("Authentication method not supported: " + request.getMethod());
}
//获取用户名和密码封装到Employee对象中
Employee emp = null;
try {
emp = JSON.parseObject(request.getInputStream(), Employee.class);
System.out.println("SecurityLoginFilter:: 页面传递上来的对象:" + emp);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("SecurityLoginFilter-emp = " + emp);
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken authRequest = new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(emp.getUsername(), emp.getPassword());
// Allow subclasses to set the "details" property
setDetails(request, authRequest);
return this.getAuthenticationManager().authenticate(authRequest);
}
}7. 编写认证授权配置类
@Configuration
public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Autowired
private EmployeeDao employeeDao;
@Bean
public BCryptPasswordEncoder bCryptPasswordEncoder(){
return new BCryptPasswordEncoder();
}
/**
* 认证
* @param auth
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
//数据库认证:根据用户名去数据库查询用户信息(用户名、密码、角色身份信息)
auth.userDetailsService(username -> employeeDao.findByUsername(username));
}
/**
* 授权
* @param http
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers(urls).permitAll()
.anyRequest().authenticated()
.and().formLogin()
.loginPage("/backend/page/login/login.html")
.and().logout().logoutUrl("/employee/logout")
.logoutSuccessHandler((request,response,authentication)->{
response.setContentType("application/json;charset=utf-8");
String json = JSON.toJSONString(R.success("退出登录成功!"));
response.getWriter().write(json);
})
.and().headers().frameOptions().sameOrigin() //加入同源策略,这样即可允许页面上加载iframe子页面
.and().csrf().disable();
//使用我们自定义的用户名密码验证过滤器顶替SpringSecurity提供的过滤器
http.addFilterAt(securityLoginFilter() , UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter.class);
}
//放行规则
private final String[] urls = {
"/**/api/**/*.*",
"/**/images/**/*.*",
"/**/js/**/*.*",
"/backend/page/login/login.html",
"/front/page/login.html",
"/**/plugins/**/*.*",
"/**/styles/**/*.*",
"/**/*.ico",
"/**/fonts/**",
"/employee/login",
"/employee/logout",
"/user/sendMsg",
"/user/login"
};
@Bean
public SecurityLoginFilter securityLoginFilter () throws Exception {
//1.构建登录过滤器对象
SecurityLoginFilter filter = new SecurityLoginFilter();
//2.设置登录过滤器拦截地址
filter.setFilterProcessesUrl("/employee/login");
//3.设置认证管理员 将自定义的登录过滤器管理器加入到SpringSecurity认证管理员管理
filter.setAuthenticationManager(authenticationManagerBean());
//4.设置登录成功处理
filter.setAuthenticationSuccessHandler((req,resp,auth)->{
//用户认证成功后 会被SpringSecurity存入到一个域对象中,这个域对象就相当于session,
Employee employee = (Employee) SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication().getPrincipal();
String json = JSON.toJSONString(R.success(employee));
resp.setContentType("application/json;charset=utf-8");
resp.getWriter().write(json);
});
//5.设置登录失败处理
filter.setAuthenticationFailureHandler((req, resp ,e)->{
//账号过期、账号锁定、密码过期、账号禁用、用户名不存在、密码错误 SpringSecurity都会抛出一个指定类型的异常
resp.setContentType("application/json;charset=utf-8");
//返回json数据
R<Object> result = null;
if (e instanceof AccountExpiredException) {
//账号过期
result = R.error("账号过期!");
} else if (e instanceof BadCredentialsException) {
//密码错误
result = R.error("密码错误!");
} else if (e instanceof CredentialsExpiredException) {
//密码过期
result = R.error("密码过期!");
} else if (e instanceof DisabledException) {
//账号不可用
result = R.error("账号不可用!");
} else if (e instanceof LockedException) {
//账号锁定
result = R.error("账号锁定!");
} else if (e instanceof InternalAuthenticationServiceException) {
//用户不存在
result = R.error("用户不存在!");
}else{
//其他错误
result = R.error("未知错误!");
}
String json = JSON.toJSONString(result);
resp.getWriter().write(json);
});
return filter;
}
}8. 修改公共字段填充
//把这个类交给spring管理
@Component
public class CommonFieldHandler implements MetaObjectHandler {
@Override
public void insertFill(MetaObject metaObject) {
System.out.println("添加操作::: 来调用insertFill给公共字段赋值了!~~!");
metaObject.setValue("createTime", LocalDateTime.now());
metaObject.setValue("updateTime", LocalDateTime.now());
//从springsecurity作用域对象中获取当前管理的认证用户对象【相当于session中存储】
Employee e = (Employee) SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication().getPrincipal();
metaObject.setValue("createUser" , e.getId());
metaObject.setValue("updateUser" , e.getId());
}
//当mybatisplus 执行更新操作的时候,会通过这个方法给公共字段赋值。
@Override
public void updateFill(MetaObject metaObject) {
metaObject.setValue("updateTime", LocalDateTime.now());
//从springsecurity中获取数据
Employee e = (Employee) SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication().getPrincipal();
metaObject.setValue("updateUser" ,e.getId());
}
}9. 使用动态鉴权
- 在category的添加分类方法上,使用注解标记需要什么样的权限才能访问该方法。
/**
* 添加分类
* @param category
* @return
*/
@PreAuthorize("hasRole('ADMIN')")
@PostMapping
public R<String> add(@RequestBody Category category){
//1. 调用service
int row = cs.add(category);
//2. 返回
if(row > 0 ){
return R.success("添加分类成功!");
}else{
return R.error("添加分类失败!");
}
}- 启动类添加开启全局注解开关
@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(prePostEnabled = true) //启用全局方法安全注解
@EnableTransactionManagement //启用事务注解驱动支持
@ServletComponentScan //将 Servlet、Filter 交由 Spring 容器管理
@MapperScan("com.itheima.dao") //扫描dao包
@Slf4j
@SpringBootApplication
public class ReggieApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(ReggieApplication.class, args);
log.info("项目启动成功!");
}
}


